Source: Information Technology Technical Secretariat (ITTS)
URL:www.itec.gov.om

If these risks should occur and cause unauthorised access and service interruptions, not only could the business or organisation be adversely affected, but the entire system could be brought to a halt. While reaping the benefits from the advances of the IT revolution, it is vital for each organisation to be cognisant of the importance of information security.
What's an Information Security Management System?
One definition would be: the protection of information assets from unauthorised access or modification of information, whether in storage, processing, or transit, and against the denial of service to authorised users or the provision of service to unauthorised users, including those measures necessary to detect, document and counter such threats.
 Security Triangle:
Security Triangle:
Confidentiality - Integrity - Availability
» Confidentiality concerns the protection of sensitive information from unauthorised disclosure.
» Integrity relates to the accuracy and completeness of information as well as to its validity in accordance with business values and expectations.
» Availability relates to information being available when required by the business process now and in the future. It also concerns the safeguarding of necessary resources and associated capabilities.
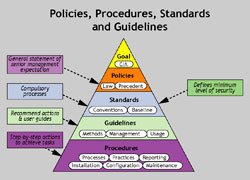
Policy Framework
 Information security frameworks are based on existing, accepted standards, guidelines and collections of practices and reflect the behaviour of an initial community of high performing organisations.
Information security frameworks are based on existing, accepted standards, guidelines and collections of practices and reflect the behaviour of an initial community of high performing organisations.
The Security and Audit Office based at ITTS has developed an information security framework built around BS7799, COBIT, NIST and ITIL models. BS7799 is the information security model which covers ten domains with 127 controls. The domains included are security policy, security organisation, asset classification and control, personnel security, physical and environment security, communications and operations management, access control, systems development and maintenance, business continuity planning and compliance.
COBIT is the control framework, IT Governance model and a maturity model which comprises of 04 domains and 34 IT processes with over 324 controls with 5 different maturity levels.
ITIL is a model for improving IT service and delivery processes which includes service support processes such as service desk, incident, problem, configuration, change and release management. Service delivery process areas include capacity, availability and financial management, service level management and IT service continuity management.
NIST standards and guidelines are the minimum baseline standards developed for securing specific products and IT process areas.
Policies
Policies define why information security is important to an organisation and describe high-level information security philosophy and topical coverage. Policies are brief, technology and solution-independent documents and rarely change (in response to new technology or threats).
Procedures
Procedures describe how to implement the standard and are the detailed, step-by-step instructions. Procedures are subject to regular change and must be maintained properly.
Standards
Standards define acceptable level of security for a specific policy area and may be technology or solution-specific. Standards provide more measurable criteria for satisfying higher level policy objectives.
Guidelines
Guidelines provide interim guidance and act as a temporary standard. Guidelines enable guidance for new technology or vulnerability or threat during creation of formal governance.
The ITTS Security and Audit Office provides documents related to information security policies, procedures, standards and guidelines to all Oman-based government ministries and government agencies.
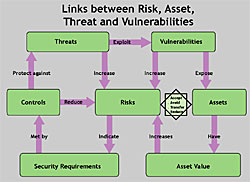
 Links between Risks, Threats & Vulnerabilities
Links between Risks, Threats & Vulnerabilities
Each organisation has information assets and each asset has a value. As the asset value increases, the risk of loss due to modification, theft or unauthorised access or unavailability increases. Increased risk implies that there needs to be security requirements which are met by deploying adequate controls. The control deployed might be a deterrent, preventive, corrective or detective control or a combination of one or more types.
Threats are agents which try to exploit the inherent flaws within the system, application, process flows which are referred to as vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities expose the assets thereby increasing risks.
Since threats are trying to exploit vulnerabilities, risk becomes higher if the threat is almost certain. Indeed, by deploying adequate controls, the risk to an organisation's assets can be reduced. Risk management involves action taken including determining the strategy to reduce, accept, transfer and avoid risks when appropriate.








